| Size of the Industry | Indian Railways operates 7,566 locomotives,37,840 Coach vehicles and 222,147 freight wagons. There are a total of 6,853 stations; 300 yards; 2,300 goods-sheds; 700 repair shops and a total workforce of 1.54 million. |
| Geographical distribution | Mumbai (Bombay), Chennai (Madras), Kolkata (Calcutta), Delhi, Hyderabad and Pune. |
| Output per annum | Revenue to Rs 57,863.90 crore |
| Market capitalization | 2.3% of GDP |
In the year 1851, the first train in India became operational and was used for the hauling of construction material in Roorkee. Then a few years later, in 1853, the first passenger train between Bori Bunder, Bombay and Thana covering a distance of 34 km (21 miles) was inaugurated, which formally gave a way to the birth of Railways in India.

In the year 1907 for the first time in its history, the Railways began to make a tidy profit and almost all the rail companies were taken over by the government. As the First World War struck the railways were used to meet the needs of the British outside India.
In 1952 total of six zones came under Indian Railway. As India improved its economy almost all railway production units were indigenised. During 1985, steam locomotives were phased out in favor of diesel and electric locomotives. In 1995 railway reservation system was streamlined with Computerization.

Many cities in the states all over the country have their own dedicated suburban networks to cater to commuters. Currently, suburban networks operate in Mumbai (Bombay), Chennai (Madras), Kolkata (Calcutta), Delhi, Hyderabad and Pune.
In India Kharagpur railway station is regarded as being the world's longest railway platform at 833 m (2,733 ft). Ghum station along with the Toy Train route is the second highest railway station in the world to be reached by a steam locomotive. The shortest named station is Lb and the longest is Sri Venkatanarasimharajuvariapeta. Himsagar Express between Kanyakumari and Jammu Tawi, is longest run train in terms of distance and time on Indian Railways network which covers 3,745 km (2,327 miles) in about 74 hours and 55 minutes.
The Trivandrum Rajdhani train travels non-stop between Vadodara and Kota, covering a distance of 528 km (328 miles) in about 6.5 hours. It has the longest continuous run on Indian Railways. The fastest train in India is the Bhopal Shatabdi Express having a maximum speed of 140 km/h (87 mph) on the Faridabad-Agra section. The fastest speed attained by any train is 184 km/h (114 mph) in 2000 during test runs.
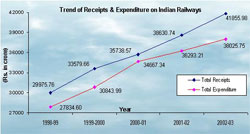
The Indian railway Industry has registered 13.87 % growth in revenue to Rs 57,863.90 crore in the first nine months ended December 31, 2008. While total earnings from freight increased by 14.53% at Rs 39,085.22 crore during the period, passenger revenue earnings were up 11.81% at Rs 16,242.44 crore. The railways have enhanced freight revenue by increasing its axle loading, improving customer services and adopting an innovative pricing strategy.
|
Indian Railways Industry is one of the largest rail networks in the world with total 63,465 route kilometers at the end of 2005-06. In 2005-06 it has handled total 666.5m tonnes of cargo and around 5,832m passenger traffic. Indian Railways is the largest Indian public sector undertaking and largest railway system in Asia run with 12000 trains a day & 63000 route kms of track. Indian Railways has around 7000 railway stations. It takes up the task of carrying nearly 11 million passengers and 1.2 million tonnes of cargo per day.
|
|
Number of Public Sector Corporations help Indian Railways to maintain, develop and modernize its systems. These corporations are also ideal employers for a variety of job applicants. These companies are:
- Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)
- Container Corporation of India
- Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation
- Indian Railways Catering and Tourism Corporation
- IRCON International Ltd.
- Konkan Railway Corporation
- Rail Land Development Authority
- Rail Vikas Nigam Limited
- Railtel Corporation of India
- RITES Ltd.
Railway Recruitment Boards conduct the mass recruitment of operational staff positions in Railways. The following are the Railway Recruitment Boards:
- Railway Recruitment Boards Ahmedabad
- Railway Recruitment Boards Ajmer
- Railway Recruitment Boards Allahabad
- Railway Recruitment Boards Bangalore
- Railway Recruitment Boards Bhopal
- Railway Recruitment Boards Bhubaneswar
- Railway Recruitment Boards Chandigarh
- Railway Recruitment Boards Chennai
- Railway Recruitment Boards Gorakhpur
- Railway Recruitment Boards Guwahati
- Railway Recruitment Boards Jammu & Srinagar
- Railway Recruitment Boards Kolkata
- Railway Recruitment Boards Malda
- Railway Recruitment Boards Mumbai
- Railway Recruitment Boards Muzaffarpur
- Railway Recruitment Boards Patna
- Railway Recruitment Boards Ranchi
- Railway Recruitment Boards Secunderabad
- Railway Recruitment Boards Thiruvananthapuram
Indian Railways Industry is divided in to 16 railway zones, which has the aim of efficient carrying out of operations, construction and maintenance of coaches, railroad construction, recruitment and maintenance of workforce. Each single zone is headed by a General Manager who reports to the Railway Board office. For each single zone there are Divisional Offices headed by Railway Divisional Managers who get the reports from divisional officer cadres such as divisional officer engineering, mechanical divisional officers, electrical divisional officers, signal & telecommunication divisional officers, divisional accounting officers & divisional personnel.
- The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, a narrow gauge train with a steam locomotive is classified as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. The route starts at Siliguri in the plains in West Bengal and traverses tea gardens en route to Darjeeling, a hill station at an elevation of 2,134 metres (7,000 ft).
- UNESCO has classified Nilgiri Hills in southern India, the Nilgiri Mountain Railway as a World Heritage.
- The Chatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus) railway station in Mumbai is another World Heritage Site operated by Indian Railways classified by UNESCO.
- In Rajasthan it is the Palace on Wheels which is a specially designed train, lugged by a steam engine, for promoting tourism in the state.
- The efforts of Maharashtra government had made a way to introduce the Deccan Odyssey along the Konkan route.
- Then there is even the Samjhauta Express a train that runs between India and Pakistan. However, in 2001 the hostilities between the two nations saw the line being closed, though it is scheduled to be opened soon.
- "Hospital-on-Wheels" Lifeline Express is a special train which provides healthcare to the rural areas. The train has a compartment that serves as an operating room, a second one which serves as a storeroom and an additional two that serve as a patient ward. The train travels around the country, staying at a location for about two months before moving elsewhere.
 Recent Press Release
Recent Press Release
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
 INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
Indian Industries



 INDIAN RAILWAY INDUSTRY
INDIAN RAILWAY INDUSTRY